Characteristics Of Congenital Heart Disease

Congenital heart disease is a problem that affects about 1% of newborns. It occurs during pregnancy when the baby’s heart develops. In case you do not already know, “congenital” means that the disease is already present at birth.
Statistics indicate that congenital heart disease is the most common disease at birth. Thanks to the development of science, the number of adults with this problem is currently greater than babies born with it.
This means that more people survive this condition. Of course, those who survive and become adults require constant monitoring in order to avoid complications.
What exactly are congenital heart diseases?
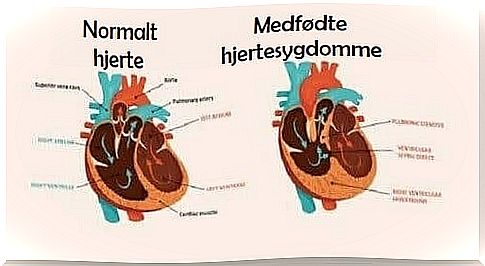
You may think that congenital heart disease is a single disorder, but there are many variations of it. It is, in fact, a group of diseases whose common characteristic is the presence of structural changes in the heart.
These changes occur due to defects in the formation of the organ during the fetal period. For example, the baby’s heart begins to form from conception, but it is not until the eighth week of pregnancy that its development is complete.
Usually, a series of successful stages must be completed when a heart is being developed. Generally, congenital heart disease occurs when some of these stages are not performed in time. Thus, the result is an abnormal heart.
Causes
In the majority of cases, it is impossible to determine the specific cause of congenital heart disease. Despite this, the World Health Organization points out that some factors increase the risk of getting one of these disorders. These are:
- Genetic factors: Family history increases the risk of developing congenital heart disease. Likewise, they are typically part of a chromosomal or genetic syndrome, such as Down syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome or others.
- Infections: When the mother has infections, such as syphilis or rubella, the risk of the fetus suffering from malformations increases.
- Nutritional status: This is when the mother is either overweight or has an excess of vitamin A or a lack of ioidines or folic acid. She may also have a disease, such as diabetes mellitus, which increases the likelihood of abnormal fetal development.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, consumption of alcohol and / or tobacco, and the use of certain drugs increase the risk of developing congenital diseases.
Symptoms and types of congenital heart disease
The symptoms of heart disease occur either immediately after birth or a few months later. Its primary symptoms in a newborn baby are:
- Problems eating
- Fast breathing
- Purple or bluish lips
- Inhibited growth
The different types of congenital heart disease can be divided into three groups:
- Problems due to excessive blood flow through the lungs. There is an increase in the pressure and exertion in the lungs in these types of disorders. They include problems such as:
- Persistent arterial canal
- Interarticular or interventricular communication
- Atrioventricular duct
- Problems with poor blood flow through the lungs. Because of this, the body does not get enough oxygen. Thus, it leads to a blue or purple color on the lips. This can lead to problems such as:
- Tricuspid atresia
- Pulmonary atresia
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Fallot Tetralogi
- Double right ventricular outlet
- Arterial trunk
- Problems due to poor blood flow in the body. Malformed heart vessels or blockages in the blood vessels prevent the passage of blood in the body. They include coarctatio aortae and narrowing of the aortic valve.
Other information to consider
To prevent congenital heart disease, a expectant mother should go for regular checkups during pregnancy. They should also only take medicines prescribed by authorized doctors who monitor them and they should try to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals.
If the pregnant woman has diabetes mellitus, she should keep her blood sugar levels under control. No matter how much a person takes care of themselves, however, it is sometimes inevitable to prevent congenital heart disease. This is because genetic factors play a big role in this.
Congenital heart disease has different levels. It all depends on the nature and degree of the deformity. Sometimes the disorders can resolve on their own when the baby is born, and other times you can control them as the baby grows.