Nutritional Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes

Nutritional therapy plays an important role in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Although many factors influence the development of this disease, a good diet is essential to control it and prevent related complications.
What should you know about it? Let’s take a closer look!
What is type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease that manifests itself in blood glucose levels that are higher than the recommended levels. In the specific case of type 2 diabetes, the body stops using insulin properly.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas and whose function is to help glucose enter the cells and be used as energy.
Among the risk factors for developing this health problem are: Having a family history of diabetes mellitus, age, obesity and physical inactivity. In fact , it is common for people with type 2 diabetes to be overweight or obese.
In these patients, it is beneficial to reduce the amount of energy in the diet while maintaining an adequate and healthy intake of nutrients at meals to promote weight loss. A weight loss can bring benefits for both glycemic control and blood pressure control.
Nutrition management in type 2 diabetes
As there is no ideal pattern for all patients or a percentage of macronutrients that can be used in general, the most advisable treatment according to the current documentation will be a common plan for food and physical activity prescribed by a professional. This is evident from research published in the journal BMJ.
According to the latest consensus from the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the goals of nutritional treatment should be the following:
- Improves parameters of glycosylated hemoglobin, reduces high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight (to this point, patient compliance and change of habits are of particular interest).
- Prevent complications.
Therefore , one of the points to be taken into account when diagnosing the disease is the dietary factor.
Carbohydrates
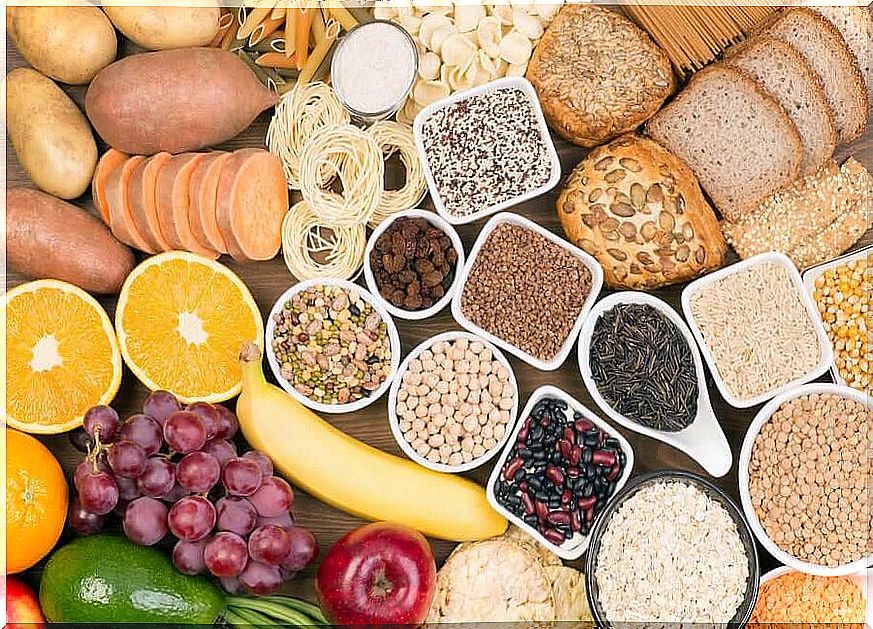

Fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains. These foods should be the main source of carbohydrate in any healthy diet, but especially for these patients. As they are partly composed of fibers, they enter the bloodstream more slowly and there are no high increases in blood glucose.
In addition, they increase the feeling of satiety, which helps with weight control. According to research published in the journal Nutrients , fiber intake appears to have a beneficial effect on serum cholesterol levels and other causes of risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure.
Therefore , doctors recommend an intake of approx. 26 grams a day in women with type 2 diabetes. In men with this health problem, they recommend 28 grams a day.
This is not the case with foods rich in simple carbohydrates where we would find cakes, sweets, fruit juices, etc. These foods are devoid of fiber and therefore their impact on glycemia is greater.
The consumption of whole grain products (cereal products that retain their three parts, germ, bran and endosperm) has been studied, and although there is insufficient evidence to justify better glycemic control of their intake, they have been linked to a decrease in systemic inflammation and mortality.
Calorie-free sweeteners
Although studies claim that calorie-free sweeteners like sukrin or stevia do not alter glycemic function, many of the foods that contain them may alter glycemic function due to the ingredients used in the production of the product.
Used as a sugar substitute , they can be beneficial in reducing the consumption of sucrose or “white sugar,” although researchers need to conduct several studies to confirm this.
Nutritional treatment: Other foods
With regard to other foods, the recommendations are the same as for the general population. As for proteins, they should also be adapted to the individual.
However, the recommendations are the same as for the rest of the population. In fact, intake of proteins of high biological value could be associated with an improvement in the insulin response without increasing plasma glycemia.
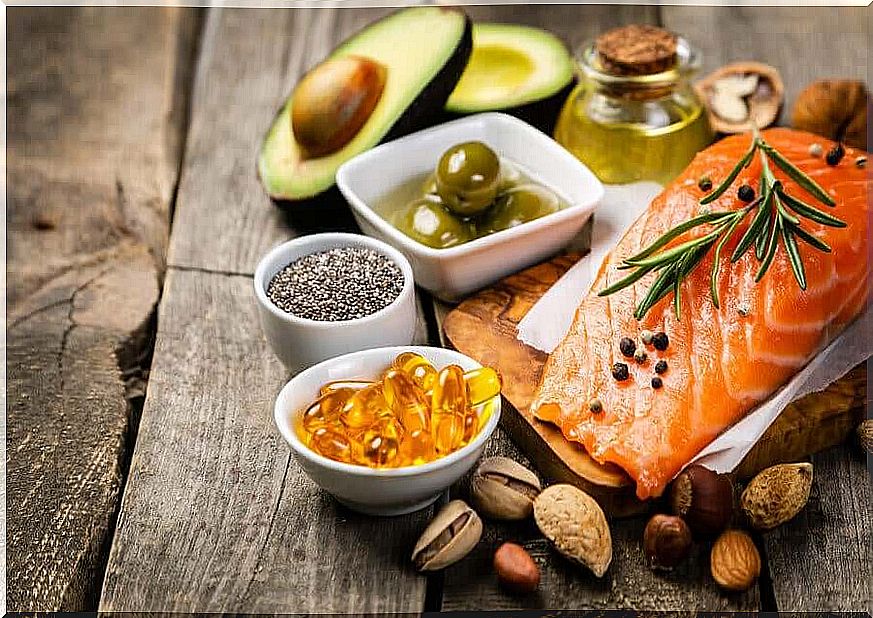
In terms of fat, as in the case of protein, the evidence suggests that it is not so much the quantity as the quality of the protein that is important.
You should consume more good quality fats (seeds, avocados, fatty fish, etc.) and reduce them of poorer quality, such as. found in processed meats and ready meals. This is essential for proper nutritional treatment.

Other recommendations for nutritional treatment of type 2 diabetes include:
- Choice of healthy dishes where the carbohydrates have a low glycemic index.
- Control of foods rich in trans fats and saturated fats due to their association with increased dyslipidemia.
- For fish, especially oily fish, the recommendation is the same as for people who do not suffer from diabetes. Due to its omega-3 fatty acid content, doctors recommend eating fatty fish at least twice a week.
- To reduce the risk of dyslipidemia, specialists also recommend eating foods rich in sterols (usually fortified), always as part of a healthy diet.
- Moderate consumption of dairy products. Fermented products (such as yogurt and cheese) appear to be particularly beneficial in controlling and preventing type 2 diabetes.
Tips for nutritional treatment of type 2 diabetes
Many patients with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese. An adapted diet plan along with physical exercise is essential to reduce weight and reduce the risk of complications.
In general, one can e.g. give the following tips:
- Make a meal distribution using fresh and healthy foods. Always consider the patient’s preferences and characteristics.
- Reduce the consumption of specific foods for people with diabetes. These are usually low in fiber and rich in poor quality fats so they cannot be considered healthy foods. Take them only occasionally.
- Reduce free sugar such as. “Table sugar” (sucrose) and foods rich in sugar. Some examples are cakes, pastries, sweets, ice cream, sugary breakfast products and juices. Also reduce ready meals, ready-made sauces, etc., as in addition to containing a large amount of sugar, they are also rich in trans fats, saturated fats and salt. Instead, we suggest that you learn how to make your own foods, where you remove or replace sugar with other foods. eg. sweetening with fruit.

- For people taking insulin, insist on nutrition education to balance insulin dose and carbohydrate intake.
- It is important to avoid alcohol as it may increase the risk of hypoglycaemia in these patients. This is especially important if they are being treated with insulin.
- With regard to salt , the recommendation for the general population also applies to patients with diabetes. Pay special attention to those people who also suffer from high blood pressure. In the latter case, they should reduce salt consumption as much as possible. Use other flavorings such as spices.
Nutritional treatment of type 2 diabetes
With type 2 diabetes, one can improve his condition with the help of a good diet. Nutritional treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes must be individually tailored, as it depends on the characteristics of the individual patient.
In general, however, one should follow some guidelines. Some examples are choosing a good source of carbohydrates, excluding sources of sugar and trans fatty acids, moderating the total calorie intake, etc.